Getting Started Tutorial
Extensions are made of different, but cohesive, components. Components can include background scripts, content scripts, an options page, UI elements and various logic files. Extension components are created with web development technologies: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. An extension's components will depend on its functionality and may not require every option.
This tutorial will build an extension that allows the user to change the background color of any page on developer.chrome.com. It will use many core components to give an introductory demonstration of their relationships.
To start, create a new directory to hold the extension's files.
The completed extension can be downloaded here.
Create the Manifest
Extensions start with their manifest.
Create a file called manifest.json
and include the following code,
or download the file
here.
{
"name": "Getting Started Example",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "Build an Extension!",
"manifest_version": 2
}
The directory holding the manifest file can be added as an extension in developer mode in its current state.
-
Open the Extension Management page by
navigating to
chrome://extensions.- The Extension Management page can also be opened by clicking on the Chrome menu, hovering over More Tools then selecting Extensions.
- Enable Developer Mode by clicking the toggle switch next to Developer mode.
- Click the LOAD UNPACKED button and select the extension directory.
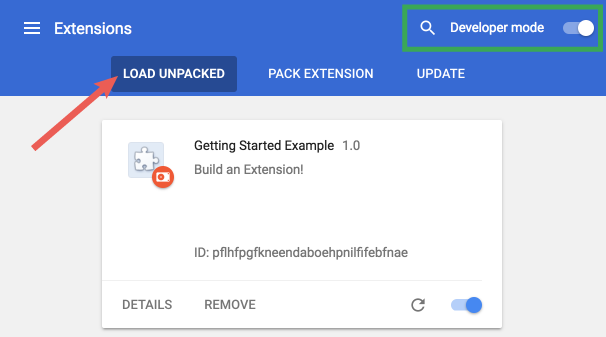
Ta-da! The extension has been successfully installed. Because no icons were included in the manifest, a generic toolbar icon will be created for the extension.
Add Instruction
Although the extension has been installed,
it has no instruction.
Introduce a background script
by creating a file titled background.js,
or downloading it
here,
and placing it inside the extension directory.
Background scripts, and many other important components, must be registered in the manifest. Registering a background script in the manifest tells the extension which file to reference, and how that file should behave.
{
"name": "Getting Started Example",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "Build an Extension!",
"background": {
"scripts": ["background.js"],
"persistent": false
},
"manifest_version": 2
}
The extension is now aware that it includes a non-persistent background script and will scan the registered file for important events it needs to listen for.
This extension will need information from a persistent variable
as soon as its installed.
Start by including a listening event for
runtime.onInstalled
in the background script.
Inside the onInstalled listener,
the extension will set a value using the
storage API.
This will allow multiple extension components to access that value
and update it.
chrome.runtime.onInstalled.addListener(function() {
chrome.storage.sync.set({color: '#3aa757'}, function() {
console.log("The color is green.");
});
});
Most APIs,
including the storage API,
must be registered under the "permissions" field in the manifest
for the extension to use them.
{
"name": "Getting Started Example",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "Build an Extension!",
"permissions": ["storage"],
"background": {
"scripts": ["background.js"],
"persistent": false
},
"manifest_version": 2
}
Navigate back to the extension management page and click the Reload link. A new field, Inspect views, becomes available with a blue link, background page.
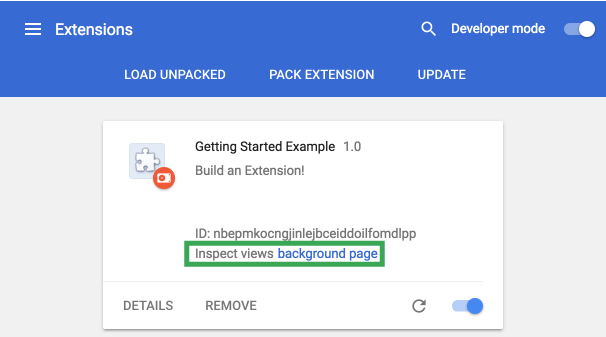
Click the link to view the background script's console log,
"The color is green."
Introduce a User Interface
Extensions can have many forms of a
user interface,
but this one will use a
popup.
Create and add a file titled popup.html to the directory,
or download it
here.
This extension uses a button to change the background color.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
button {
height: 30px;
width: 30px;
outline: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="changeColor"></button>
</body>
</html>
Like the background script,
this file needs to be designated as a popup in the manifest under
page_action.
{
"name": "Getting Started Example",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "Build an Extension!",
"permissions": ["storage"],
"background": {
"scripts": ["background.js"],
"persistent": false
},
"page_action": {
"default_popup": "popup.html"
},
"manifest_version": 2
}
Designation for toolbar icons is also included under page_action
in the default_icons field.
Download the images folder
here,
unzip it,
and place it in the extension's directory.
Update the manifest so the extension knows how to use the images.
{
"name": "Getting Started Example",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "Build an Extension!",
"permissions": ["storage"],
"background": {
"scripts": ["background.js"],
"persistent": false
},
"page_action": {
"default_popup": "popup.html",
"default_icon": {
"16": "images/get_started16.png",
"32": "images/get_started32.png",
"48": "images/get_started48.png",
"128": "images/get_started128.png"
}
},
"manifest_version": 2
}
Extensions also display images on the extension management page,
the permissions warning,
and favicon.
These images are designated in the manifest under
icons.
{
"name": "Getting Started Example",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "Build an Extension!",
"permissions": ["storage"],
"background": {
"scripts": ["background.js"],
"persistent": false
},
"page_action": {
"default_popup": "popup.html",
"default_icon": {
"16": "images/get_started16.png",
"32": "images/get_started32.png",
"48": "images/get_started48.png",
"128": "images/get_started128.png"
}
},
"icons": {
"16": "images/get_started16.png",
"32": "images/get_started32.png",
"48": "images/get_started48.png",
"128": "images/get_started128.png"
},
"manifest_version": 2
}
If the extension is reloaded at this stage,
it will include a grey-scale icon,
but will not contain any functionality differences.
Because page_action is declared in the manifest,
it is up to the extension to tell the browser when the user can interact
with popup.html.
Add declared rules to the background script with the
declarativeContent
API within the
runtime.onInstalled listener event.
chrome.runtime.onInstalled.addListener(function() {
chrome.storage.sync.set({color: '#3aa757'}, function() {
console.log('The color is green.');
});
chrome.declarativeContent.onPageChanged.removeRules(undefined, function() {
chrome.declarativeContent.onPageChanged.addRules([{
conditions: [new chrome.declarativeContent.PageStateMatcher({
pageUrl: {hostEquals: 'developer.chrome.com'},
})
],
actions: [new chrome.declarativeContent.ShowPageAction()]
}]);
});
});
The extension will need permission to access the
declarativeContent API
in its manifest.
{
"name": "Getting Started Example",
...
"permissions": ["declarativeContent", "storage"],
...
}

The browser will now show a full-color page action icon in the browser
toolbar when users navigate to a URL that contains
"developer.chrome.com".
When the icon is full-color, users can click it to view popup.html.
The last step for the popup UI is adding color to the button.
Create and add a file called
popup.js with the following code to the extension directory,
or downloaded
here.
let changeColor = document.getElementById('changeColor');
chrome.storage.sync.get('color', function(data) {
changeColor.style.backgroundColor = data.color;
changeColor.setAttribute('value', data.color);
});
This code grabs the button from popup.html
and requests the color value from storage.
It then applies the color as the background of the button.
Include a script tag to popup.js in popup.html.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
...
<body>
<button id="changeColor"></button>
<script src="popup.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Reload the extension to view the green button.
Layer Logic
The extension now knows the popup should be available to users on
developer.chrome.com
and displays a colored button,
but needs logic for further user interaction.
Update popup.js to include the following code.
let changeColor = document.getElementById('changeColor');
...
changeColor.onclick = function(element) {
let color = element.target.value;
chrome.tabs.query({active: true, currentWindow: true}, function(tabs) {
chrome.tabs.executeScript(
tabs[0].id,
{code: 'document.body.style.backgroundColor = "' + color + '";'});
});
};
The updated code adds an onclick event the button, which triggers a programatically injected content script. This turns the background color of the page the same color as the button. Using programmatic injection allows for user-invoked content scripts, instead of auto inserting unwanted code into web pages.
The manifest will need the activeTab
permission to allow the extension temporary access to the
tabs API.
This enables the extension to call
tabs.executeScript.
{
"name": "Getting Started Example",
...
"permissions": ["activeTab", "declarativeContent", "storage"],
...
}
The extension is now fully functional! Reload the extension, refresh this page, open the popup and click the button to turn it green! However, some users may want to change the background to a different color.
Give Users Options
The extension currently only allows users to change the background to green. Including an options page gives users more control over the extension's functionality, further customizing their browsing experience.
Start by creating a file in the directory called options.html
and include the following code, or download it
here.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
button {
height: 30px;
width: 30px;
outline: none;
margin: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="buttonDiv">
</div>
<div>
<p>Choose a different background color!</p>
</div>
</body>
<script src="options.js"></script>
</html>
Then register the options page in the manifest,
{
"name": "Getting Started Example",
...
"options_page": "options.html",
...
"manifest_version": 2
}
Reload the extension and click DETAILS.
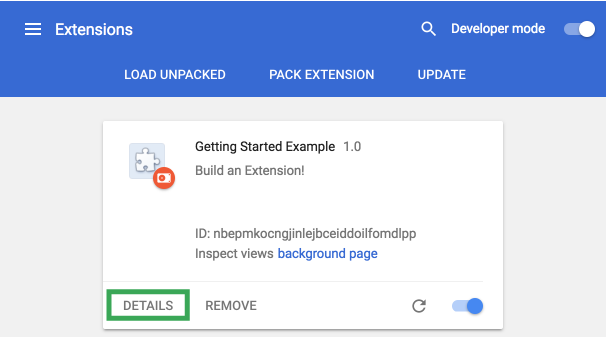
Scroll down the details page and select Extension options to view the options page, although it will currently appear blank.
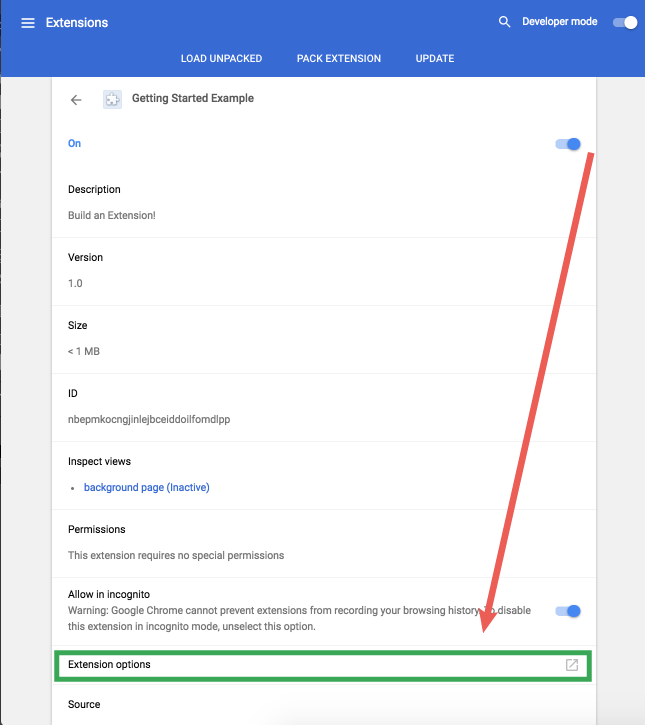
Last step is to add the options logic.
Create a file called options.js in the extension directory
with the following code,
or download it
here.
let page = document.getElementById('buttonDiv');
const kButtonColors = ['#3aa757', '#e8453c', '#f9bb2d', '#4688f1'];
function constructOptions(kButtonColors) {
for (let item of kButtonColors) {
let button = document.createElement('button');
button.style.backgroundColor = item;
button.addEventListener('click', function() {
chrome.storage.sync.set({color: item}, function() {
console.log('color is ' + item);
})
});
page.appendChild(button);
}
}
constructOptions(kButtonColors);
Four color options are provided then generated as buttons on the options page with onclick event listeners. When the user clicks a button, it updates the color value in the extension's global storage. Since all of the extension's files pull the color information from global storage no other values need to be updated.
Take the Next Step
Congratulations! The directory now holds a fully-functional, albeit simplistic, Chrome extension.
What's next?
-
The Chrome Extension Overview backs up a bit, and fills in a lot of detail about the Extensions architecture in general, and some specific concepts developers will want to be familiar with.
-
Learn about the options available for debugging Extensions in the debugging tutorial.
-
Chrome Extensions have access to powerful APIs above and beyond what's available on the open web. The chrome.* APIs documentation will walk through each API.
-
The developer's guide has dozens of additional links to pieces of documentation relevant to advanced extension creation.
