chrome.certificateProvider
| Description: |
Use this API to expose certificates to the platform which can use these
certificates for TLS authentications.
|
| Availability: |
Since Chrome 46.
|
| Permissions: |
"certificateProvider"
|
Important: This API works only on Chrome OS.
Usage
Typical usage of this API to expose client certificates to Chrome OS follows these steps:
- The Extension registers for the events onCertificatesRequested and onSignDigestRequested.
- During a TLS handshake, the browser receives a client certificate request. With a onCertificatesRequested event, the browser asks the Extension to report all certificates that it currently provides.
- The Extension reports back with the currently available certificates, using the callback that was provided with the event.
- The browser matches all available certificates with the client certificate request from the remote host. The matches are presented to the user in a selection dialog.
- The user can select a certificate and thereby approve the authentication
or abort the authentication.
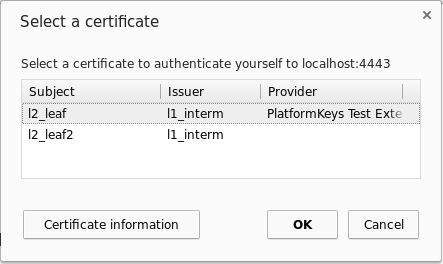
- If the user aborts the authentication or no certificate matched the request, the TLS client authentication is aborted.
- Otherwise, if the user approves the authentication with a certificate provided by this Extension, the browser requests the Extension to sign a digest to continue the TLS handshake. The request is sent as a onSignDigestRequested event.
- This event contains a digest, declares which hash function was used to create the digest, and refers to one of the certificates that were reported by this Extension in reaction to the most recent certificate request. The Extension must create a signature for the given digest using the private key associated with the referenced certificate. Creating the signature might require prepending a DigestInfo and padding the result before the actual signing.
- The Extension sends back the signature to the browser using the callback that was provided as part of the event. If the signature couldn't be calculated, the callback is called without signature.
- If the signature was provided, the browser completes the TLS handshake.
The actual sequence of steps can be different. For example, the user will not be asked to select a certificate if the enterprise policy to automatically select a certificate is used (see AutoSelectCertificateForUrls and Chrome policies for users).
In the Extension, this can look similar to the following snippet:
function onCertificatesRejected(rejectedCerts) {
// If certificates were rejected by the API, log an error, for example.
console.error(rejectedCerts.length + ' certificates were rejected.');
}
function reportCertificates(reportCallback) {
var certs = [];
// Fill |certs| with all certificates that this Extension provides.
// For example:
var certInfo = {
certificate: new Uint8Array(...),
supportedHashes: ['SHA256']
};
certs.push(certInfo);
reportCallback(certs, function(rejectedCerts) {
if (chrome.runtime.lastError) {
// Handle API errors, like argument type errors.
return;
}
if (rejectedCerts.length !== 0)
onCertificatesRejected(rejectedCerts);
});
}
// Returns a private key handle for the given DER-encoded certificate.
// |certificate| is an ArrayBuffer.
function getPrivateKeyHandle(certificate) {...}
// If required, prepends |digest| with a DigestInfo and pads the result
// according to the key type and the given Hash function.
// |digest| is an ArrayBuffer. |hash| is a Hash. Returns an ArrayBuffer.
function prepareDigest(digest, hash) {...}
// Signs |digest| with the given private key. |digest| is an ArrayBuffer.
// Returns the signature as ArrayBuffer.
function signDigest(privateKey, digest) {...}
function reportSignature(signRequest, reportCallback) {
// Look up the handle to the private key of |signRequest.certificate|.
var key = getPrivateKeyHandle(signRequest.certificate);
if (!key) {
// Handle if the key isn't available.
console.error('Key for requested certificate no available.');
// Abort the request by reporting the error to the API.
reportCallback();
return;
}
var preparedDigest = prepareDigest(signRequest.digest, signRequest.hash);
var signature = signDigest(key, preparedDigest);
reportCallback(signature);
}
chrome.certificateProvider.onCertificatesRequested.addListener(
reportCertificates);
chrome.certificateProvider.onSignDigestRequested.addListener(
reportSignature);
Summary
| Types | |
|---|---|
| Hash | |
| PinRequestErrorType | |
| CertificateInfo | |
| SignRequest | |
| Methods | |
requestPin −
chrome.certificateProvider.requestPin(object details, function callback)
| |
stopPinRequest −
chrome.certificateProvider.stopPinRequest(object details, function callback)
| |
setCertificates −
chrome.certificateProvider.setCertificates(array of CertificateInfo certificates, function callback)
| |
| Events | |
| onCertificatesRequested | |
| onSignDigestRequested | |
Types
Hash
| Enum |
|---|
"MD5_SHA1",
"SHA1",
"SHA256",
"SHA384",
or "SHA512"
|
PinRequestErrorType
| Enum |
|---|
"INVALID_PIN",
"INVALID_PUK",
"MAX_ATTEMPTS_EXCEEDED",
or "UNKNOWN_ERROR"
|
CertificateInfo
| properties | ||
|---|---|---|
| ArrayBuffer | certificate |
Must be the DER encoding of a X.509 certificate. Currently, only certificates of RSA keys are supported. |
| array of Hash | supportedHashes |
Must be set to all hashes supported for this certificate. This extension will only be asked for signatures of digests calculated with one of these hash algorithms. This should be in order of decreasing hash preference. |
SignRequest
| properties | ||
|---|---|---|
| integer | signRequestId |
Since Chrome 57. The unique ID to be used by the extension should it need to call a method that requires it, e.g. requestPin. |
| ArrayBuffer | digest |
The digest that must be signed. |
| Hash | hash |
Refers to the hash algorithm that was used to create |
| ArrayBuffer | certificate |
The DER encoding of a X.509 certificate. The extension must sign |
Methods
requestPin
chrome.certificateProvider.requestPin(object details, function callback)
Since Chrome 57.
Requests the PIN from the user. Only one ongoing request at a time is allowed. The requests issued while another flow is ongoing are rejected. It's the extension's responsibility to try again later if another flow is in progress.
| Parameters | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| object | details |
Contains the details about the requested dialog.
|
||||||||||||
| function | callback |
Is called when the dialog is resolved with the user input, or when the dialog request finishes unsuccessfully (e.g. the dialog was canceled by the user or was not allowed to be shown). The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(object details) {...};
|
||||||||||||
stopPinRequest
chrome.certificateProvider.stopPinRequest(object details, function callback)
Since Chrome 57.
Stops the pin request started by the requestPin function.
| Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| object | details |
Contains the details about the reason for stopping the request flow.
|
||||||
| function | callback |
To be used by Chrome to send to the extension the status from their request to close PIN dialog for user. The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function() {...};
|
||||||
setCertificates
chrome.certificateProvider.setCertificates(array of CertificateInfo certificates, function callback)
Not fully implemented. You must build Chromium from source to try this API. Learn more.
Sets a list of certificates to use in the browser.
| Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| array of CertificateInfo | certificates |
The list of certificates to set. Invalid certificates will be ignored. |
| function | (optional) callback |
Called upon completion. If you specify the callback parameter, it should be a function that looks like this: function() {...};
|
Events
onCertificatesRequested
Since Chrome 47.
This event fires every time the browser requests the current list of certificates provided by this extension. The extension must call reportCallback exactly once with the current list of certificates.
addListener
chrome.certificateProvider.onCertificatesRequested.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function(function reportCallback) {...};
|
||||||
onSignDigestRequested
This event fires every time the browser needs to sign a message using a certificate provided by this extension in reply to an onCertificatesRequested event. The extension must sign the data in request using the appropriate algorithm and private key and return it by calling reportCallback. reportCallback must be called exactly once.
addListener
chrome.certificateProvider.onSignDigestRequested.addListener(function callback)
| Parameters | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | callback |
The callback parameter should be a function that looks like this: function( SignRequest request, function reportCallback) {...};
|
|||||||||
